13.6 L 100km To Mpg
braininterpreter
Sep 17, 2025 · 7 min read
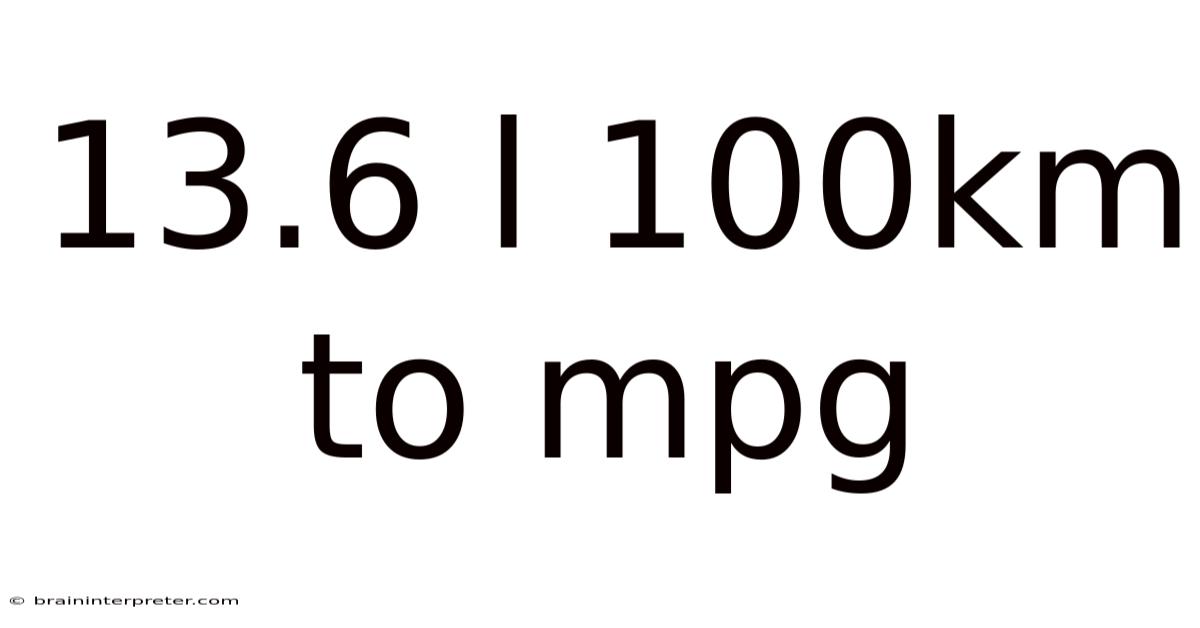
Table of Contents
Decoding Fuel Efficiency: Converting 13.6 L/100km to MPG and Understanding Fuel Consumption
Are you tired of seeing fuel consumption figures in liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km) and wishing you could understand them in the more familiar miles per gallon (MPG)? This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 13.6 L/100km to MPG but also delve into the science behind fuel efficiency, helping you understand what factors influence your car's gas mileage and how to improve it. We'll explore the calculation, its implications, and answer frequently asked questions, providing a complete picture of fuel consumption and its relevance to your driving experience.
Understanding Liters per 100 Kilometers (L/100km)
The metric system uses liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km) to express fuel economy. This indicates how many liters of fuel a vehicle consumes while traveling 100 kilometers. A lower L/100km figure signifies better fuel efficiency—your car is using less fuel to cover the same distance.
Understanding Miles per Gallon (MPG)
The imperial system, commonly used in the United States and some other countries, uses miles per gallon (MPG) to express fuel economy. This represents how many miles a vehicle can travel on one gallon of fuel. A higher MPG figure indicates better fuel efficiency.
Converting 13.6 L/100km to MPG: The Calculation
Converting L/100km to MPG requires a straightforward calculation. Here's the formula:
MPG = (235.21) / (L/100km)
Let's apply this to our example:
MPG = (235.21) / (13.6)
MPG ≈ 17.3
Therefore, 13.6 L/100km is approximately equivalent to 17.3 MPG. This means a vehicle with a fuel consumption of 13.6 L/100km can travel roughly 17.3 miles on one gallon of fuel.
Factors Influencing Fuel Consumption
Several factors influence a vehicle's fuel consumption, leading to variations from the manufacturer's stated figures. Understanding these factors can help you improve your fuel efficiency and potentially save money.
-
Driving Style: Aggressive driving habits like rapid acceleration, hard braking, and excessive speeding significantly increase fuel consumption. Smooth, consistent driving is key to better fuel efficiency.
-
Vehicle Weight: Heavier vehicles require more energy to move, resulting in lower fuel economy. Carrying unnecessary weight in your car also impacts fuel consumption.
-
Vehicle Type: Different vehicle types have different levels of inherent efficiency. Smaller, lighter vehicles generally achieve better fuel economy than larger, heavier ones like SUVs or trucks. Aerodynamics also play a crucial role; a more aerodynamic vehicle will experience less wind resistance, leading to better fuel efficiency.
-
Tire Pressure: Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, improving fuel efficiency. Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance, forcing the engine to work harder and consuming more fuel.
-
Engine Size and Type: Larger engines generally consume more fuel than smaller ones. The type of engine (e.g., gasoline, diesel, hybrid) also impacts fuel efficiency; hybrid and electric vehicles are often significantly more fuel-efficient than conventional gasoline-powered cars.
-
Terrain and Road Conditions: Driving uphill, navigating steep inclines, and driving on rough or unpaved roads increases fuel consumption. Traffic congestion and stop-and-go driving also contribute to lower fuel economy.
-
Climate Control: Using the air conditioner consumes extra fuel, especially in warmer climates. Using it sparingly or opting for alternative ventilation methods can improve fuel efficiency.
-
Vehicle Maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as oil changes, filter replacements, and tire rotations, ensures optimal engine performance and contributes to better fuel economy. Ignoring maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency and potentially costly repairs.
Improving Fuel Efficiency: Practical Tips
Improving your car's fuel economy is not only environmentally responsible but can also save you money on fuel costs. Here are several practical tips you can implement:
-
Drive Smoothly: Avoid aggressive driving habits. Accelerate and brake gradually, maintain a consistent speed whenever possible, and anticipate traffic conditions to minimize sudden stops and starts.
-
Maintain Proper Tire Pressure: Regularly check and inflate your tires to the recommended pressure specified in your vehicle's owner's manual. Proper inflation reduces rolling resistance and improves fuel economy.
-
Reduce Unnecessary Weight: Remove any unnecessary items from your car to reduce its overall weight. This can significantly improve fuel efficiency, especially on longer journeys.
-
Optimize Your Route: Plan your routes to avoid traffic congestion and unnecessary detours. Using navigation apps can help you find the most efficient route.
-
Use Cruise Control (When Appropriate): On highways or long stretches of open road, cruise control can help maintain a consistent speed, improving fuel economy. However, avoid using cruise control in congested areas or on winding roads.
-
Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Follow the recommended maintenance schedule in your owner's manual. Regular servicing keeps your car running efficiently, maximizing fuel economy.
-
Consider Your Driving Habits: Analyze your driving patterns. Identify areas where you can improve and consciously work on adopting more fuel-efficient driving techniques.
-
Use Air Conditioning Sparingly: Use the air conditioner only when necessary. Open windows for ventilation whenever possible, especially at lower speeds.
-
Keep Your Engine Tuned: A well-maintained engine burns fuel more efficiently. Regular tune-ups can improve fuel economy.
Scientific Explanation of Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a complex interplay of several scientific principles:
-
Thermodynamics: The efficiency of an internal combustion engine is governed by the laws of thermodynamics. Heat energy from the combustion of fuel is converted into mechanical energy to power the vehicle. However, some energy is lost as heat, friction, and other inefficiencies. Engine design and technology play a crucial role in minimizing these energy losses.
-
Aerodynamics: The shape and design of a vehicle significantly impact its aerodynamic drag. Aerodynamic drag is the resistance a vehicle encounters as it moves through the air. Reducing aerodynamic drag improves fuel efficiency by reducing the energy required to overcome this resistance. Features like streamlined body shapes and aerodynamic components help minimize drag.
-
Rolling Resistance: Rolling resistance is the friction between the tires and the road surface. Factors such as tire pressure, tire tread, and road surface condition affect rolling resistance. Lower rolling resistance leads to improved fuel efficiency.
-
Engine Technology: Modern engine technologies, such as direct injection, variable valve timing, and turbocharging, contribute to improved fuel efficiency by optimizing combustion and reducing energy losses. Hybrid and electric vehicles offer further advancements in fuel efficiency by utilizing alternative power sources and regenerative braking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is 17.3 MPG good fuel economy?
A: Whether 17.3 MPG is considered good depends on the type of vehicle. For a larger SUV or truck, it might be average or slightly below average. However, for a smaller sedan or hatchback, it might be considered below average. It's crucial to compare it to the fuel economy of similar vehicles.
Q: How can I accurately calculate my own MPG?
A: To calculate your own MPG, fill your fuel tank completely. Record the odometer reading. Drive your vehicle until you need to refuel again. Fill the tank completely once more and note the amount of fuel added and the new odometer reading. Subtract the initial odometer reading from the final reading to get the miles driven. Divide the miles driven by the gallons of fuel added to determine your MPG.
Q: What are some alternative units for measuring fuel consumption?
A: Besides L/100km and MPG, other units used include kilometers per liter (km/L), and gallons per 100 miles (gal/100mi).
Q: How does temperature affect fuel efficiency?
A: Cold weather can slightly reduce fuel efficiency due to increased engine warm-up time and thicker oil viscosity. Extremely hot weather can also impact fuel efficiency due to increased use of air conditioning.
Conclusion
Understanding fuel efficiency is crucial for both environmental and economic reasons. Converting 13.6 L/100km to MPG provides a clearer picture of a vehicle's fuel consumption, allowing for better comparisons and informed decision-making. By understanding the factors influencing fuel economy and implementing practical tips for improvement, drivers can optimize their vehicle's performance, reduce their environmental footprint, and save money on fuel costs. Remember that consistent effort and mindful driving habits significantly contribute to achieving better fuel efficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 2 Cups A Pint
Sep 17, 2025
-
How Long Is 20 M
Sep 17, 2025
-
June 24 2005 Nakastra Birthday
Sep 17, 2025
-
30 An Hour To Salary
Sep 17, 2025
-
20 00 Per Hour Annual Salary
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 13.6 L 100km To Mpg . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.